Comprehensive guide to improving corporate onboarding
In this guide we will examine the key aspects of onboarding, the key steps in the process, the role of the IT department, and how Deepser simplifies the IT department's operations. We will pay special attention to the increasingly central role of technology and the IT department, essential elements in meeting the challenges of hybrid…
What is corporate onboarding
Corporate onboarding is the process by which a new employee is introduced and integrated into an organization. It is the moment when a new person officially joins the company, becoming familiar with the work environment, its dynamics and its people.
This process is often underestimated, but it is not simply a matter of assigning a location or handing over documents and devices. On the contrary, it encompasses a series of strategic activities designed to foster the integration of the new employee, putting him or her in the ideal condition to become operational and productive in the shortest possible time.
Why onboarding is so important
Onboarding represents one of the most important moments in a new hire’s work life, a pivot point that can determine the success or failure of the new employee’s integration.
Welcoming a new member to the team is a multifaceted process that goes far beyond a simple operational introduction: it includes the transmission of corporate values and culture. Effectively communicating the organization’s values is key to helping the new employee understand the company’s priorities and mission, fostering a deeper emotional and professional connection to the work environment. This approach not only reinforces a sense of belonging, but also helps create a harmonious alignment between personal and company expectations.
Moreover, the value of well-designed onboarding is reflected in its ability to build a lasting bond between the employee and the company. For example, onboarding that includes mentoring sessions, ongoing training and regular feedback not only increases initial productivity but also fosters a sense of belonging and job satisfaction.
The stages of corporate onboarding
Effective onboarding unfolds in several interconnected stages, each playing a critical role in overall success:
1. Pre-arrival preparation
The first phase is pre-arrival preparation, which begins even before the new employee sets foot in the company. This phase includes gathering and organizing the necessary documentation and planning a customized induction program. The most attentive companies often give on arrival or send a welcome kit directly to the employee’s home, to make him or her feel an integral part of the team right away.
2. Reception and orientation
This is followed by the welcome and orientation phase, a crucial time to put the new employee at ease and familiarize him or her with the work environment. A guided tour of the company space familiarizes the employee with the office and its resources, while introductions to team members help create an initial interpersonal bond and better understand roles and dynamics. This phase is also an opportunity to illustrate daily routines, share key tools and procedures, and answer any questions.
3. Initial Training
Initial training is the third phase of the onboarding process and is crucial in providing the new employee with the concrete tools needed to learn the skills required by the role. This moment is not limited to a simple knowledge transfer, but aims to create an engaging and tailored learning experience. In fact, many companies leverage digital platforms and innovative technologies to make training more dynamic and interactive, integrating e-learning modules, webinars, and hands-on simulations
4. Cultural integration
The fourth phase is focused to cultural integration, a key aspect of ensuring that the new employee does not feel like an outsider but an integral part of the organization. This phase relies on targeted activities such as team building, which fosters collaboration and trust among colleagues, informal meetings to encourage spontaneous and authentic relationships, and participation in company events that reinforce a sense of community. Well-planned cultural integration not only helps the new employee internalize the company’s values and traditions, but also creates an environment in which he or she can fulfill his or her potential.
How to optimize onboarding
Effective onboarding relies on meticulous attention to detail and a holistic approach capable of considering every aspect of a new employee’s induction. Clarity of expectations plays a crucial role: new employees need to understand precisely what their goals are, how to measure their contribution, and what resources and supports the company provides for their success.
How to manage onboarding in remote teams
In the case of remote work, an additional layer of complexity is added. When team members do not meet in person, it becomes more difficult to build authentic bonds and foster a sense of belonging.
In these cases, it is essential to leverage virtual communication technologies, such as video calls and collaboration tools, to create opportunities for meaningful interaction. Organizing informal virtual meetings or online team building sessions can help bridge the gap and strengthen interpersonal relationships.
In addition, for remote teams, it is especially important to provide detailed onboarding on the systems and technology tools that will be used. Ensuring that each new employee is comfortable with the company’s digital platforms helps reduce isolation and foster greater efficiency. Dedicated technical support and the availability of a virtual mentor can make a big difference in ensuring that newcomers feel supported even at a distance.
How long should onboarding be?
The duration of corporate onboarding cannot be defined uniquely, as it depends on various factors, including the complexity of the role, organizational dynamics and the size of the company. However, regardless of the specific duration, the first few months are of crucial importance to the success of the new hire.
Well-structured onboarding that continues beyond the first few weeks ensures that the new employee feels valued and prepared, thereby increasing his or her engagement and likelihood of long-term success.
Many successful organizations opt for an extended approach, extending the process for up to six months or even a year. This strategy allows for the integration of ongoing training, learning opportunities and regular progress monitoring.
The role of IT in onboarding
The importance of the IT department is often underestimated, despite the fact that it is one of the key pillars of effective onboarding. Well-structured technology support is essential to ensure that new employees have access to the tools and resources they need from day one, enabling them to be up and running immediately.
The IT team plays a key role in this process, handling not only the configuration and delivery of devices, such as laptops, smartphones or tablets, but also ensuring that they are fully ready to use. It is also in charge of setting up corporate accounts, such as email addresses and access to internal platforms, and setting up safe and secure virtual environments
One crucial aspect is cybersecurity. Ensuring that all devices are configured securely and that new employees receive training on company data protection policies is essential to avoid vulnerabilities.
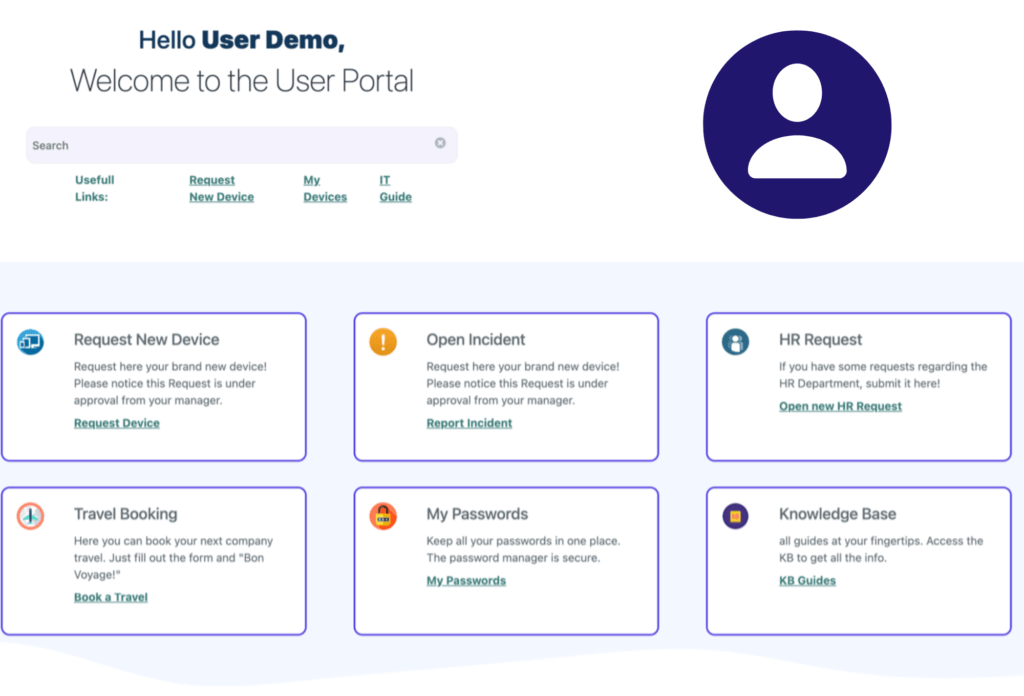
In addition, very often the IT department is also tasked with handling employee support requests, a central element in maintaining high operational efficiency. In these cases, IT makes use of a user portal where employees can create structured support requests on their own. This solution not only simplifies the work of the IT team, but also provides employees with a clear and accessible point of reference.
How Deepser supports the IT department
Deepser offers an innovative solution designed to simplify and enhance the work of the IT department.
With Deepser, the IT team can manage all support requests, whether they come via Email or from the User Portal, within a centralized and organized system. Each ticket is tracked and managed accurately, ensuring fast response times and high-quality service. This approach not only improves operational efficiency, but also helps boost overall productivity and increase satisfaction within the company.
The User Portal is highly customizable, allowing each field to be tailored to the specific needs of each company. This flexibility allows employees to create requests in a structured manner, improving the clarity of communications and reducing resolution times. The result is a more efficient IT team and more satisfied employees.
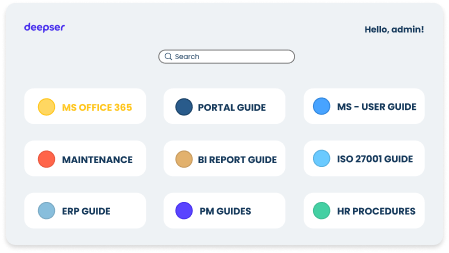
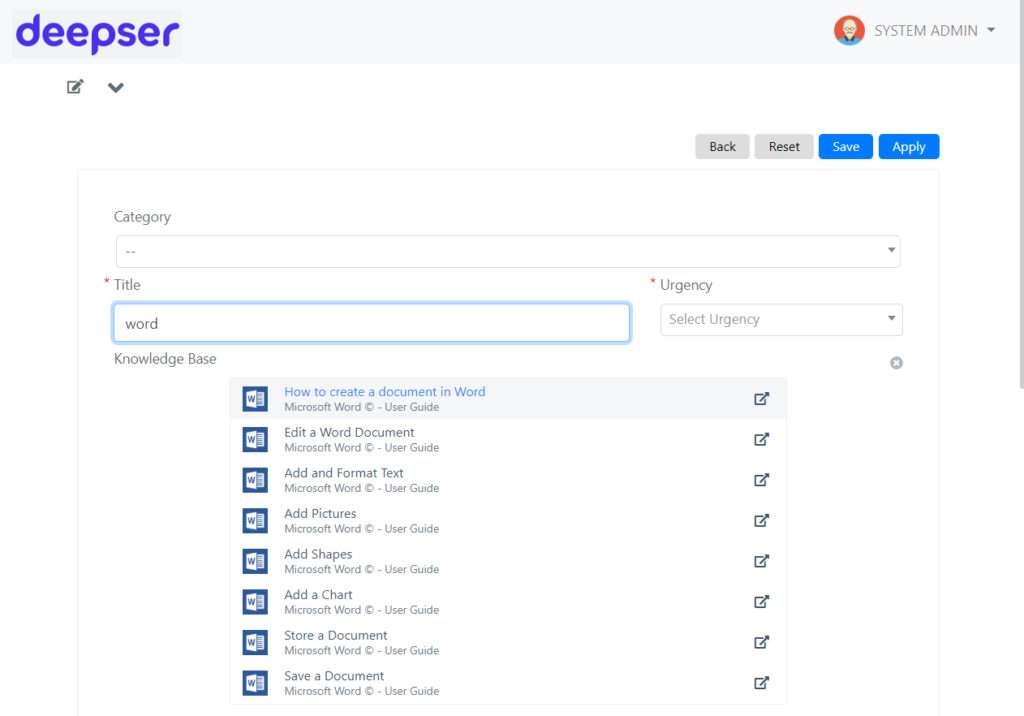
The integrated Knowledge Base is a valuable resource for documenting procedures and solutions. It is useful not only to the IT department, but to the entire company. In the case of onboarding, offering new employees immediate access to guides and training materials for faster and more effective integration.
The IT Asset Management module then enables management of employee-assigned devices, such as laptops and smartphones. Providing a detailed view of the status and location of assets, reducing downtime and optimizing IT infrastructure management.
Together, these features make Deepser a comprehensive solution for improving business efficiency and organization.
Tips to improve the onboarding process
Onboarding is a dynamic process that requires constant monitoring and adaptation to ensure its effectiveness. An essential first step is to collect feedback from employees who have completed the process. This allows you to identify not only areas for improvement, but also positive aspects to be enhanced. Showing employees that their opinion is heard and valued strengthens their sense of belonging and trust in the organization.
Integrating specific metrics to measure onboarding success is equally important. Among the key metrics to monitor, the time it takes new hires to reach full productivity provides an indication of how quickly the process prepares them to be effective in their role. Other useful metrics include employee retention rates and overall satisfaction levels as measured by periodic surveys.
Conclusion
Investing in well-structured onboarding is not only a best practice, but a necessity for companies that want to attract and retain top talent. A thorough and personalized process not only improves the employee experience, but also contributes directly to productivity and overall business success.
If you want to simplify and streamline IT process management for corporate onboarding and beyond, Deepser offers everything you need. With its advanced features, you can monitor every aspect of the process, improve the productivity of your IT team, and ensure a positive experience for new employees.
Book a free demo now and see how Deepser simplifies IT management, credit card not required!